A kilometre comes to mind in any discussion of distance. A kilogram for weight & a minute for time. A metric is therefore a tool for measuring units of any thing measurable.
Having measures of business activity is critical. It gives dimension to understand business aspects like income & expenses in relation to time & money.
Approach
Use of metrics requires properly collected business data through effective book keeping measures. This is critical for the accuracy & success of business metrics.
The following steps will lead to identification & use of business metrics;
- Install a spreadsheet software program. Microsoft Excel is our choice of software.
Microsoft Excel is an accessible spreadsheet program.
- Create a new spreadsheet & add data to the tables from the business data source
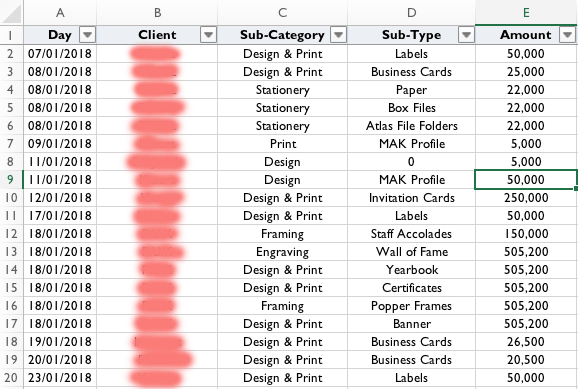
A sample of data from a book keeping source for business income
- With the data in place, identify a measurable data point for example days, weeks & months & relate it to another metric for example revenue. Metrics developed from this example are revenue per day, revenue per week or revenue per month. These metrics shape the understanding of business revenue from the defined periods of time.
Commonly Used Metrics
Plenty of metrics are used to measure business activity which vary in application & complexity. A few commonly used metrics include;
Gross Profit
This is the measure of the profit off a sale minus expenses.
A pen bought for sale at 500/- & sold at 1000/- will have a Gross profit of 500/- (1000-500).
This metric provides an understanding of the profit potential of a business.
Net Profit
This a measure of the general performance of the business.
A pen bought for sale at 500/- & sold at 1000/- with a packaging expense of 400/- will have a Net Profit of 100/- (1000 – (500+400))
This provides an understanding of the viability of the business.
Profit Margins
This measures how profitable the business is. It is represented as a percentage & calculated by dividing the difference between revenue & costs of goods sold by the revenue.
A pen bought for sale at 500/- & sold at 1000/- will have a profit margin of 50% ((1000-500) / 1000).
This metric helps a business understand costing in relation to profitability. Its where the business makes money. A higher margin represents high profitability of a business & vice versa.
Operating Margin
This measures the performance of the business. It is represented as a percentage & calculated by dividing the difference between revenue & the sum of total costs & expenses of the business. The result is represented as a percentage.
A pen bought for sale at 500/- & sold at 1000/- with a packaging expense of 400/- will have an operating margin of 10% (1000 – (500+400) / 1000).
With expenses factored in, the metric gives a general understanding of the business & its activity.
Business Value of Metrics
Metrics provide a business owner with following key benefits;
- A scientific method to understanding the business, its operation & health
- Information to make accurate & informed decisions for the business
Thank You for Reading.
